Engineering Agility in Aerospace
Navigating Complexity through Digital, Agile and Sustainable Innovation
1. Executive Summary
The aerospace industry is undergoing its most significant transformation in decades. Post-pandemic recovery, sustainability mandates, digital acceleration, and rising customer expectations are redefining how aircraft are engineered, certified, and supported throughout the lifecycle.
Commercial aircraft demand is expected to grow 3–5% annually through 2040, while the industry races toward net-zero emissions by 2050 (IATA, 2023). At the same time, digital technologies—MBSE, digital twins, predictive analytics, and AI—are enabling faster development cycles and new operating models.
This whitepaper explores how agile engineering, digital technologies, and sustainable design principles are reshaping the future of aerospace. Drawing from ALTEN India’s contributions across global programs, it outlines practical frameworks for aerospace companies to build innovation-ready, globally integrated engineering ecosystems
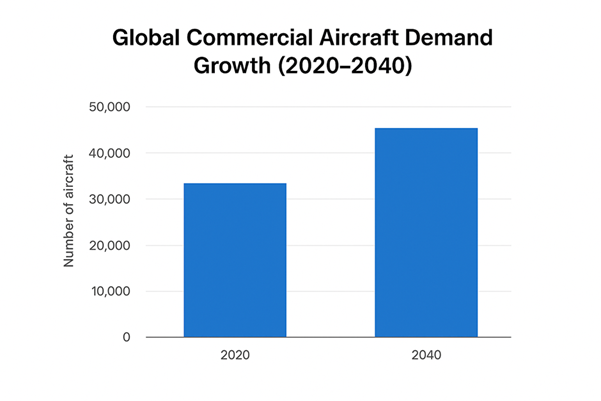
2. The Aerospace Industry at an Inflection Point
Aerospace stakeholders—from OEMs to Tier-1 suppliers—are balancing the competing demands of faster delivery, tighter regulation, and increasing complexity.
Key Challenges include:
- Sustainability Pressures: Aviation contributed 2.5% of global CO₂ emissions in 2022, and levels could triple by 2050 without strong intervention, according to the International Energy Agency.
- Digital Disruption: Research by PwC indicates that digital transformation can reduce engineering cycle times by 30–50%, reshaping competitiveness.
- Cost & Compliance Challenges: With demand for over 44,000 new aircraft by 2040 (as projected by Airbus), OEMs must accelerate delivery while ensuring stringent compliance such as DO-178C, DO-254, DO-326, ARP4761 and ARP4754A .
- Changing Customer Expectations: Airlines and passengers now expect highly personalized, connected, and environmentally conscious flying experiences.
- Electrification & Hybrid Propulsion Feasibility: The industry faces significant uncertainty around the maturity, scalability, safety, and certification pathways for electric and hybrid propulsion systems—making it one of aerospace’s most complex future-readiness challenges.
3. Rethinking Aerospace Engineering: Industry Trends
3.1 Agile Product Development
Traditional waterfall lifecycle models can’t keep pace with shifting customer expectations and evolving certification demands. Agile methodologies—especially Scrum—enable faster iteration, continuous testing, and early risk reduction. A 2023 study by Capgemini reported that aerospace software teams adopting Agile achieved 20–30% faster delivery and significantly improved stakeholder alignment.
3.2 Digital Thread & Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE)
MBSE and digital threads enable a single, integrated engineering view across design, simulation, manufacturing, and sustainment. A propulsion study by NASA (2023) showed that digital twins drove up to 40% cost reduction in system development.
3.3 Emerging Aerospace Innovation Trends
- Military & Defence Modernization Pressures
Geopolitical tensions have led to a surge in defence spending across the US, Europe, India, and APAC—creating both an opportunity and a capability challenge.
Defense aerospace programs are accelerating investments in:- Next-gen stealth platforms to maintain tactical advantage
- Advanced composites and signature-reduction engineering
- High-assurance avionics with hardened cybersecurity
- AI-enabled mission systems for real-time tactical intelligence
However, the rapid pace of technological evolution demands continuous upgrades, modular open-systems architecture (MOSA), and accelerated certification cycles—forcing OEMs to rethink traditional R&D and integration models.
- Electrification & Hybrid Propulsion
OEMs are accelerating R&D on electric and hybrid propulsion systems to meet sustainability goals. While still limited by battery density, safety, and certification challenges, these technologies represent a key pathway to reducing emissions. - Advanced Air Mobility (AAM)
AAM is transforming urban and regional transportation with new mobility formats—from autonomous shuttles to low-noise commuter aircraft—driving demand for advanced avionics, lightweight materials, and integrated traffic management. - eVTOLs & Air Taxis
Electric Vertical Takeoff and Landing (eVTOL) platforms are at the forefront of next-gen mobility. Companies working in the AAM ecosystem are pushing boundaries in battery systems, distributed propulsion, flight safety, and air-traffic integration. - Autonomous Cargo Drones
Fully autonomous and BVLOS (Beyond Visual Line of Sight) cargo drones are redefining logistics for defense, humanitarian aid, and last-mile delivery. These require advanced sensing, fault-tolerant control systems, and robust command-and-control platforms. - Cybersecurity-Driven Architectures
As aircraft become more connected and software-defined, cybersecurity is no longer optional. Protecting avionics, communication links, and onboard systems is pushing the industry toward secure-by-design architectures, zero-trust models, and next-gen threat monitoring.
3.4 Repair, MRO, and Sustainment Complexity
- Repair Challenges & MRO Modernization
With civil aviation demand rising sharply, localized repair and maintenance ecosystems are struggling to keep pace. The shift toward regionally distributed MRO hubs brings new engineering challenges:- Growing backlog of repairs due to constrained supply chains
- Need for rapid, simulation-led validation of repair schemes
- Certification limitations requiring meticulous documentation
- Integration of digital tools for faster turnaround
Advanced technologies—AI-driven fault detection, AR-assisted repair manuals, and digital twins for real-time service-state prediction—are helping accelerate repair engineering cycles by up to 30–40% in leading programs.
4. ALTEN India in Aerospace: Global Engineering in Action
4.1 Core Capabilities:
- Product Engineering: Structures, interiors, systems (CAD/CAE expertise)
- Avionics Software: DO-178B/C, DO-254, DO-326 compliant design, development & V&V
- Digital Engineering: MBSE, digital twins, data-driven MRO strategies
- Manufacturing Support: Tooling, process design, production ramp-up
- Sustainability Support: Lightweight material R&D, green system design, Obsolescence Management
4.2 Global Delivery Model:
- Hubs in Bangalore and Pune, integrated with France, Germany, and the US
- Scalable teams operating in co-engineering and standalone models
- Shared toolchains and agile practices for real-time collaboration
- 24/7 distributed engineering for accelerated delivery
- Consistent quality under AS9100D and global ALTEN standards
As per NASSCOM (2024), India is expected to contribute 20% of the global Engineering R&D workforce by 2030—positioning ALTEN India as a strategic capability hub for aerospace engineering.